

1) Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA)
- HPA는 스케일 인/아웃을 통해 파드 수를 늘리거나 줄이는 방법이다
- 쿠버네테스에서 설정한 메트릭에 따라 포드 수를 자동으로 조절한다. (예: CPU 사용률)
- 애플리케이션의 부하가 일시적으로 높아질 때 유용
- 파드 수를 늘림으로써 처리량을 높일 수 있다.
- 리소스 사용량이 증가할 수 있어 비용 효율성을 떨어뜨릴 수 있다.

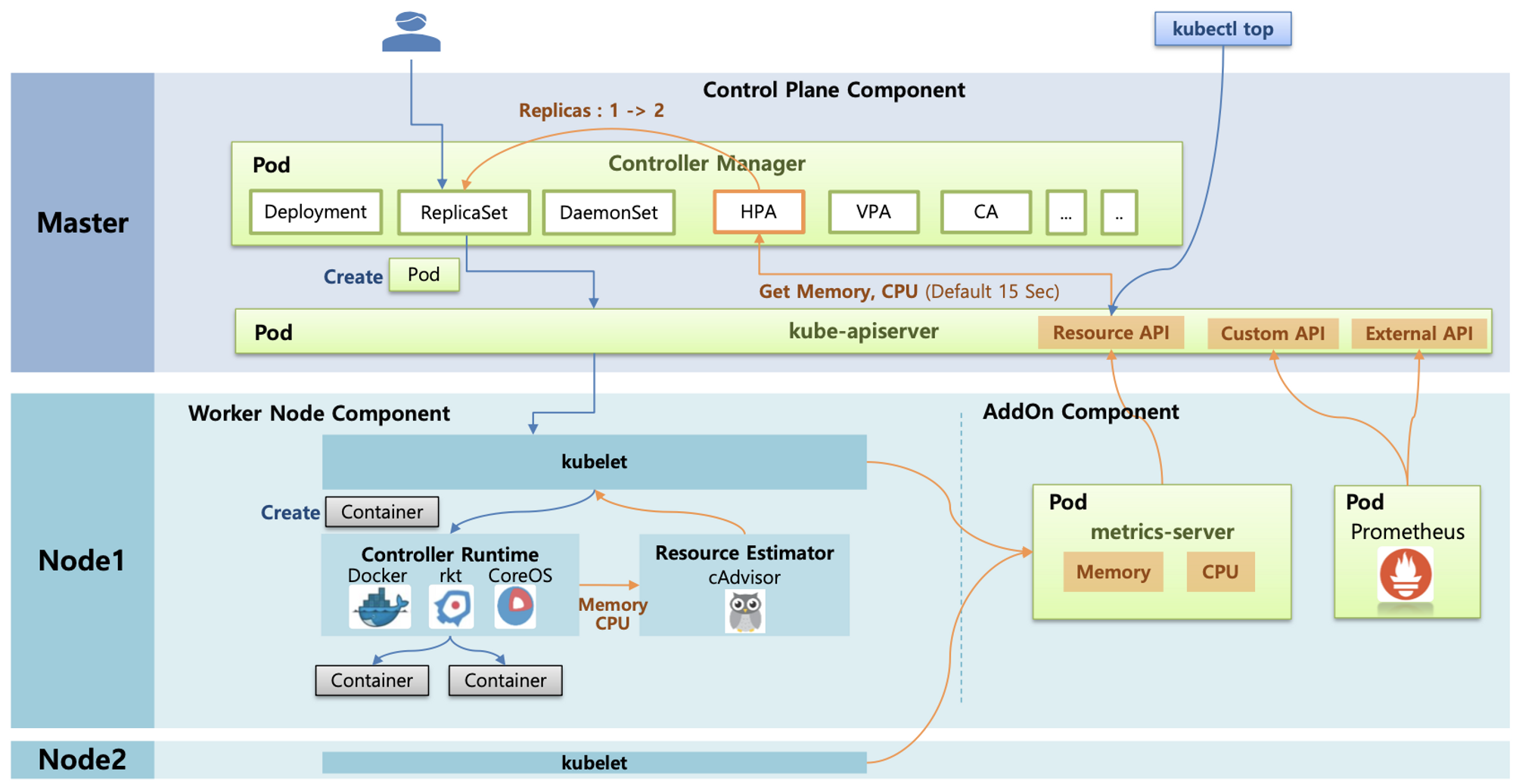
- HPA 아키텍처 : cAdvisor 이 컨테이너의 메모리/CPU 수집 → metrics-server 는 kubelet 를 통해서 수집 후 apiserver 에 등록 → HPA는 apiserver(Resource API)를 통해서 15분 마다 메모리/CPU 수집하여 정책에 따라 동작
- metrics.type(Resource, Pods, Object), target.type(Utilization, AverageValue, Value)
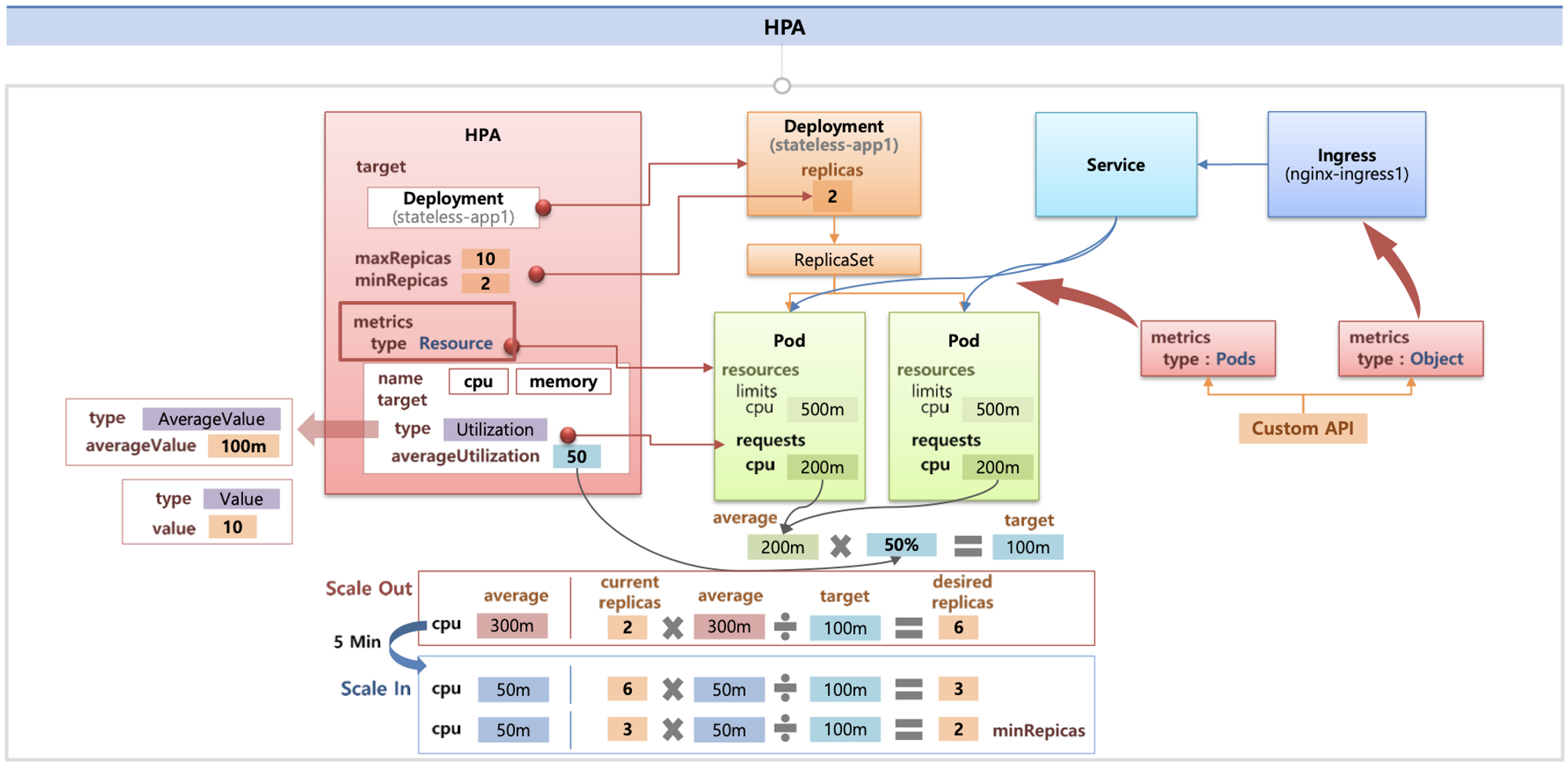
2) Vertical Pod Autoscaling (VPA)
- VPA는 포드 수는 유지하되 필요한 리소스를 늘리거나 줄이는 방법이다.
- 파드 리소스 할당량 (CPU, 메모리 등)을 기준에 따라 동적으로 조절한다. -> resource.limit ,request 값을 수정하여 최적의 값을 찾는데 도움
- 파드의 리소스 사용량이 지속적으로 변동하는 경우 사용한다.
- 리소스 사용량을 최적화하여 비용 효율을 높일 수 있다.
- 스케일 업 과정에서 재시작이 필요할 수 있어 다운타임이 발생할 수 있다.
- 흐름도 : 메트릭 서버가 용량 수집 -> 파드 최적값을 계산 -> 파드 삭제 -> 파드 생성 -> 리소스 조정

3) Cluster Autoscaling (CAS) -> Karpenter 사용
- CAS는 클러스터의 노드 수를 조절하여 Pending 상태의 파드를 Running 상태로 변경하는 방법이다.
- pending 상태의 파드가 있을 때 워커 노드를 추가하여 리소스를 확장하고, 파드를 running 상태로 변경한다.
- 클러스터 자원이 부족하거나 남는 경우 노드 수를 조절하여 사용률을 최적화한다.
- 클러스터의 처리량과 리소스 사용률을 효과적으로 관리 가능
- 노드 수의 증감으로 인한 오버헤드와 비용 변동성이 발생할 수 있다.

1. HPA - Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
# Run and expose php-apache server
curl -s -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/website/main/content/en/examples/application/php-apache.yaml
cat php-apache.yaml | yh
kubectl apply -f php-apache.yaml
# 확인
kubectl exec -it deploy/php-apache -- cat /var/www/html/index.php
...
# 모니터링 : 터미널2개 사용
watch -d 'kubectl get hpa,pod;echo;kubectl top pod;echo;kubectl top node'
kubectl exec -it deploy/php-apache -- top
# 접속
PODIP=$(kubectl get pod -l run=php-apache -o jsonpath={.items[0].status.podIP})
curl -s $PODIP; echo

# Create the HorizontalPodAutoscaler : requests.cpu=200m - 알고리즘
# Since each pod requests 200 milli-cores by kubectl run, this means an average CPU usage of 100 milli-cores.
kubectl autoscale deployment php-apache --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
kubectl describe hpa
...
Metrics: ( current / target )
resource cpu on pods (as a percentage of request): 0% (1m) / 50%
Min replicas: 1
Max replicas: 10
Deployment pods: 1 current / 1 desired
...
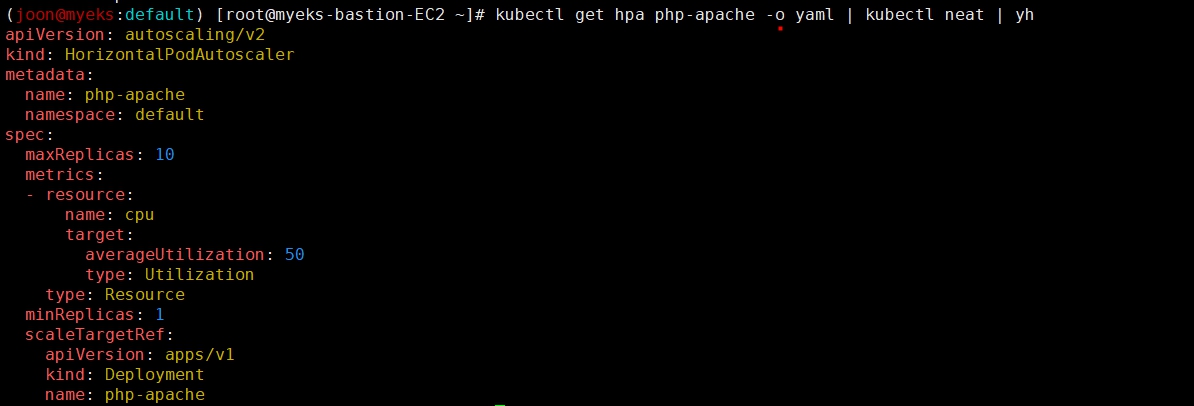
# HPA 설정 확인
kubectl krew install neat
kubectl get hpa php-apache -o yaml
kubectl get hpa php-apache -o yaml | kubectl neat | yh
spec:
minReplicas: 1 # [4] 또는 최소 1개까지 줄어들 수도 있습니다
maxReplicas: 10 # [3] 포드를 최대 5개까지 늘립니다
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache # [1] php-apache 의 자원 사용량에서
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50 # [2] CPU 활용률이 50% 이상인 경우
# 반복 접속 1 (파드1 IP로 접속) >> 증가 확인 후 중지
while true;do curl -s $PODIP; sleep 0.5; done
# 반복 접속 2 (서비스명 도메인으로 접속) >> 증가 확인(몇개까지 증가되는가? 그 이유는?) 후 중지 >> 중지 5분 후 파드 갯수 감소 확인
# Run this in a separate terminal
# so that the load generation continues and you can carry on with the rest of the steps
kubectl run -i --tty load-generator --rm --image=busybox:1.28 --restart=Never -- /bin/sh -c "while sleep 0.01; do wget -q -O- http://php-apache; done"




2. KEDA - Kubernetes based Event Driven Autoscaler
기존의 HPA(Horizontal Pod Autoscaler)는 리소스(CPU, Memory) 메트릭을 기반으로 스케일 여부를 결정한다.
반면에 KEDA는 특정 이벤트를 기반으로 스케일 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
예를 들어 airflow는 metadb를 통해 현재 실행 중이거나 대기 중인 task가 얼마나 존재하는지 알 수 있다.
이러한 이벤트를 활용하여 worker의 scale을 결정한다면 queue에 task가 많이 추가되는 시점에 더 빠르게 확장이 가능하다.

- KEDA는 쿠버네테스의 사용자 정의 리소스를 활용하여 이벤트에 따른 스케일링을 정의하고 관리한다.
- 이벤트 소스와 메트릭을 기반으로, KEDA는 수평적인 파드 자동 확장(HPA)을 지원하며, 이를 통해 자동으로 파드를 스케일 아웃/스케일 인한다.
- KEDA는 이벤트 소스로부터 메시지나 작업의 수를 추적하고, 구성된 임계값을 기반으로 파드를 확장하거나 축소한다.
- KEDA는 다양한 이벤트 소스와 큐 시스템을 지원하여, AWS SQS, Azure Storage Queue, Apache Kafka 등과 같은 서비스들도 쉽게 연동할 수 있다.
- 쿠버네테스 환경에서 서버리스 워크로드를 효과적으로 관리할 수 있으며, Knative Serving과 같은 다른 오토스케일링 패러다임과 함께 사용될 수 있다.

# KEDA 설치
cat <<EOT > keda-values.yaml
metricsServer:
useHostNetwork: true
prometheus:
metricServer:
enabled: true
port: 9022
portName: metrics
path: /metrics
serviceMonitor:
# Enables ServiceMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
podMonitor:
# Enables PodMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
operator:
enabled: true
port: 8080
serviceMonitor:
# Enables ServiceMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
podMonitor:
# Enables PodMonitor creation for the Prometheus Operator
enabled: true
webhooks:
enabled: true
port: 8080
serviceMonitor:
# Enables ServiceMonitor creation for the Prometheus webhooks
enabled: true
EOT
kubectl create namespace keda
helm repo add kedacore https://kedacore.github.io/charts
helm install keda kedacore/keda --version 2.10.2 --namespace keda -f keda-values.yaml
# KEDA 설치 확인
kubectl get-all -n keda
kubectl get crd | grep keda
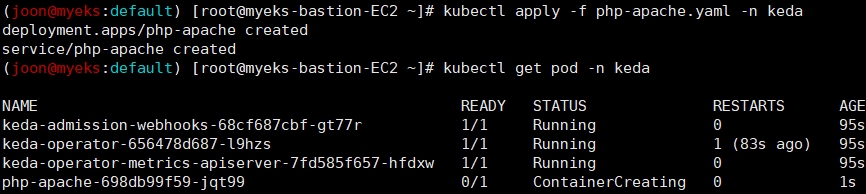
# keda 네임스페이스에 디플로이먼트 생성
kubectl apply -f php-apache.yaml -n keda
kubectl get pod -n keda
# ScaledObject 정책 생성 : cron
cat <<EOT > keda-cron.yaml
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: ScaledObject
metadata:
name: php-apache-cron-scaled
spec:
minReplicaCount: 0
maxReplicaCount: 2
pollingInterval: 30
cooldownPeriod: 300
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache
triggers:
- type: cron
metadata:
timezone: Asia/Seoul
start: 00,15,30,45 * * * *
end: 05,20,35,50 * * * *
desiredReplicas: "1"
EOT
kubectl apply -f keda-cron.yaml -n keda
# 그라파나 대시보드 추가
# 모니터링
watch -d 'kubectl get ScaledObject,hpa,pod -n keda'
kubectl get ScaledObject -w
# 확인
kubectl get ScaledObject,hpa,pod -n keda
kubectl get hpa -o jsonpath={.items[0].spec} -n keda | jq
...
"metrics": [
{
"external": {
"metric": {
"name": "s0-cron-Asia-Seoul-00,15,30,45xxxx-05,20,35,50xxxx",
"selector": {
"matchLabels": {
"scaledobject.keda.sh/name": "php-apache-cron-scaled"
}
}
},
"target": {
"averageValue": "1",
"type": "AverageValue"
}
},
"type": "External"
}
# KEDA 및 deployment 등 삭제
kubectl delete -f keda-cron.yaml -n keda && kubectl delete deploy php-apache -n keda && helm uninstall keda -n keda
kubectl delete namespace keda



# 대시보드 추가
1. https://github.com/kedacore/keda/blob/main/config/grafana/keda-dashboard.json 접속
2. 대시보드 import




3. VPA - Vertical Pod Autoscaler
- pod resources.request을 최대한 최적값으로 수정, HPA와 같이 사용 불가능, 수정 시 파드 재실행
- VPA는 파드에 할당된 리소스(CPU, 메모리 등)를 실시간 모니터링하고 해당 파드의 사용량에 따라 리소스를 조절한다.
- 최소 리소스 요구량과 최대 리소스 제한 사이에서 동적으로 스케일링을 수행하며, 예약된 및 사용 중인 리소스 사용률을 최적화한다.
- VPA가 스케일링을 위해 적용할 변경 사항이 있다면, 파드를 재시작하여 새로운 리소스로 실행할 수 있다.
# 코드 다운로드
git clone https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler.git
cd ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/
tree hack
# openssl 버전 확인
openssl version
OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
# openssl 1.1.1 이상 버전 확인
yum install openssl11 -y
openssl11 version
OpenSSL 1.1.1g FIPS 21 Apr 2020
# 스크립트파일내에 openssl11 수정
sed -i 's/openssl/openssl11/g' ~/autoscaler/vertical-pod-autoscaler/pkg/admission-controller/gencerts.sh
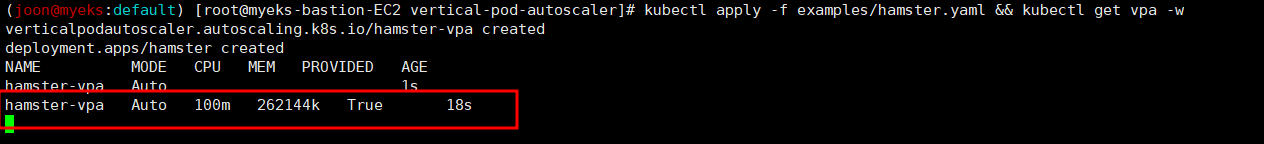
# Deploy the Vertical Pod Autoscaler to your cluster with the following command.
watch -d kubectl get pod -n kube-system
cat hack/vpa-up.sh
./hack/vpa-up.sh
kubectl get crd | grep autoscaling







4. CA - Cluster Autoscaler

- Cluster Autoscale 동작을 위한 cluster-autoscaler 파드(디플로이먼트)를 배치한다.
- Cluster Autoscaler(CA)는 pending 상태인 파드가 존재할 경우, 워커 노드를 스케일 아웃한다.
- 특정 시간을 간격으로 사용률을 확인하여 스케일 인/아웃을 수행한다. 그리고 AWS에서는 Auto Scaling Group(ASG)을 사용하여 Cluster Autoscaler를 적용한다.
- CA는 클러스터의 부족한 리소스를 감지하고 필요한만큼 노드를 추가하여 사용가능한 리소스를 확장한다.
- 반대로 여분의 리소스가 있는 경우 사용하지 않는 노드를 제거하여 리소스를 절약한다.
- 클러스터의 부하와 리소스 이용률에 따라 자동으로 노드를 확장하거나 축소한다.
- CA 문제점 : 하나의 자원에 대해 두군데 (AWS ASG vs AWS EKS)에서 각자의 방식으로 관리 ⇒ 관리 정보가 서로 동기화되지 않아 다양한 문제 발생
설정 전 확인
# EKS 노드에 이미 아래 tag가 들어가 있음
# k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled : true
# k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/myeks : owned
aws ec2 describe-instances --filters Name=tag:Name,Values=$CLUSTER_NAME-ng1-Node --query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].Tags[*]" --output yaml | yh
...
- Key: k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/myeks
Value: owned
- Key: k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled
Value: 'true'

AWS용 Cluster Autoscaler는 Auto Scaling 그룹과의 통합을 제공한다. 사용자는 다음 네 가지 배포 옵션 중 하나를 선택할 수 있다
- One Auto Scaling group
- Multiple Auto Scaling groups
- Auto-Discovery : Auto-Discovery 는 클러스터 오토스케일러를 구성하는 데 선호되는 방법이다.
- Control-plane Node setup
# 현재 autoscaling(ASG) 정보 확인
# aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='클러스터이름']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups \
--query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" \
--output table
-----------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| eks-ng1-44c41109-daa3-134c-df0e-0f28c823cb47 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
# MaxSize 6개로 수정
export ASG_NAME=$(aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].AutoScalingGroupName" --output text)
aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} --min-size 3 --desired-capacity 3 --max-size 6
# 확인
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
-----------------------------------------------------------------
| DescribeAutoScalingGroups |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
| eks-ng1-c2c41e26-6213-a429-9a58-02374389d5c3 | 3 | 6 | 3 |
+------------------------------------------------+----+----+----+
# 배포 : Deploy the Cluster Autoscaler (CA)
curl -s -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/aws/examples/cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
sed -i "s/<YOUR CLUSTER NAME>/$CLUSTER_NAME/g" cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
kubectl apply -f cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
# 확인
kubectl get pod -n kube-system | grep cluster-autoscaler
kubectl describe deployments.apps -n kube-system cluster-autoscaler
# (옵션) cluster-autoscaler 파드가 동작하는 워커 노드가 퇴출(evict) 되지 않게 설정
kubectl -n kube-system annotate deployment.apps/cluster-autoscaler cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/safe-to-evict="false"






# 모니터링
kubectl get nodes -w
while true; do kubectl get node; echo "------------------------------" ; date ; sleep 1; done
while true; do aws ec2 describe-instances --query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PrivateIPAdd:PrivateIpAddress,InstanceName:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" --filters Name=instance-state-name,Values=running --output text ; echo "------------------------------"; date; sleep 1; done
# Deploy a Sample App
# We will deploy an sample nginx application as a ReplicaSet of 1 Pod
cat <<EoF> nginx.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-to-scaleout
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
service: nginx
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx-to-scaleout
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
EoF
kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
kubectl get deployment/nginx-to-scaleout
# Scale our ReplicaSet
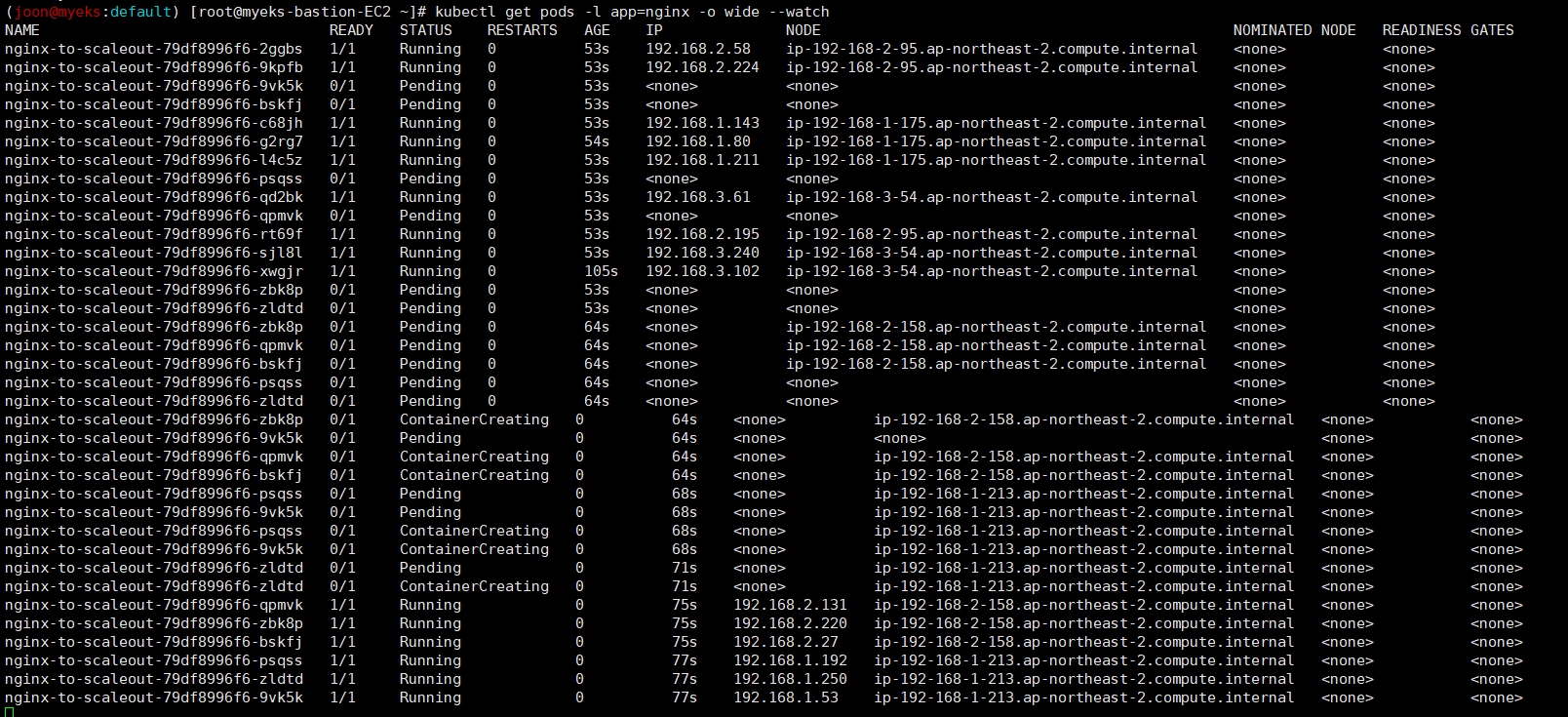
# Let’s scale out the replicaset to 15
kubectl scale --replicas=15 deployment/nginx-to-scaleout && date
# 확인
kubectl get pods -l app=nginx -o wide --watch
kubectl -n kube-system logs -f deployment/cluster-autoscaler
# 노드 자동 증가 확인
kubectl get nodes
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups \
--query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" \
--output table
./eks-node-viewer
42 pods (0 pending 42 running 42 bound)
ip-192-168-3-196.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ███████████████████████████████████ 100% (10 pods) t3.medium/$0.0520 On-Demand
ip-192-168-1-91.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu ███████████████████████████████░░░░ 89% (9 pods) t3.medium/$0.0520 On-Demand
ip-192-168-2-185.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu █████████████████████████████████░░ 95% (11 pods) t3.medium/$0.0520 On-Demand
ip-192-168-2-87.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu █████████████████████████████░░░░░░ 84% (6 pods) t3.medium/$0.0520 On-Demand
ip-192-168-3-15.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal cpu █████████████████████████████░░░░░░ 84% (6 pods) t3.medium/$0.0520 On-Demand
# 디플로이먼트 삭제
kubectl delete -f nginx.yaml && date
# 노드 갯수 축소 : 기본은 10분 후 scale down 됨, 물론 아래 flag 로 시간 수정 가능 >> 그러니 디플로이먼트 삭제 후 10분 기다리고 나서 보자!
# By default, cluster autoscaler will wait 10 minutes between scale down operations,
# you can adjust this using the --scale-down-delay-after-add, --scale-down-delay-after-delete,
# and --scale-down-delay-after-failure flag.
# E.g. --scale-down-delay-after-add=5m to decrease the scale down delay to 5 minutes after a node has been added.
# 터미널1
watch -d kubectl get node
```bash
위 실습 중 디플로이먼트 삭제 후 10분 후 노드 갯수 축소되는 것을 확인 후 아래 삭제를 해보자! >> 만약 바로 아래 CA 삭제 시 워커 노드는 4개 상태가 되어서 수동으로 2대 변경 하자!
kubectl delete -f nginx.yaml
# size 수정
aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name ${ASG_NAME} --min-size 3 --desired-capacity 3 --max-size 3
aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups --query "AutoScalingGroups[? Tags[? (Key=='eks:cluster-name') && Value=='myeks']].[AutoScalingGroupName, MinSize, MaxSize,DesiredCapacity]" --output table
# Cluster Autoscaler 삭제
kubectl delete -f cluster-autoscaler-autodiscover.yaml
```





5. CPA - Cluster Proportional Autoscaler

- 노드 수 증가에 비례하여 성능 처리가 필요한 애플리케이션(컨테이너/파드)를 수평으로 자동 확장
- CPA는 클러스터의 확장 또는 축소와 관련하여 추가 또는 삭제되는 노드 수에 따라 컨트롤 비례하도록 워크로드를 스케일한다.
- CPA는 사용자가 설정한 기준(메트릭)에 따라 워크로드를 조절한다.
- 시스템 상태를 조사하여 리소스 예약을 줄이고 글로벌 워크로드를 최적화한다.
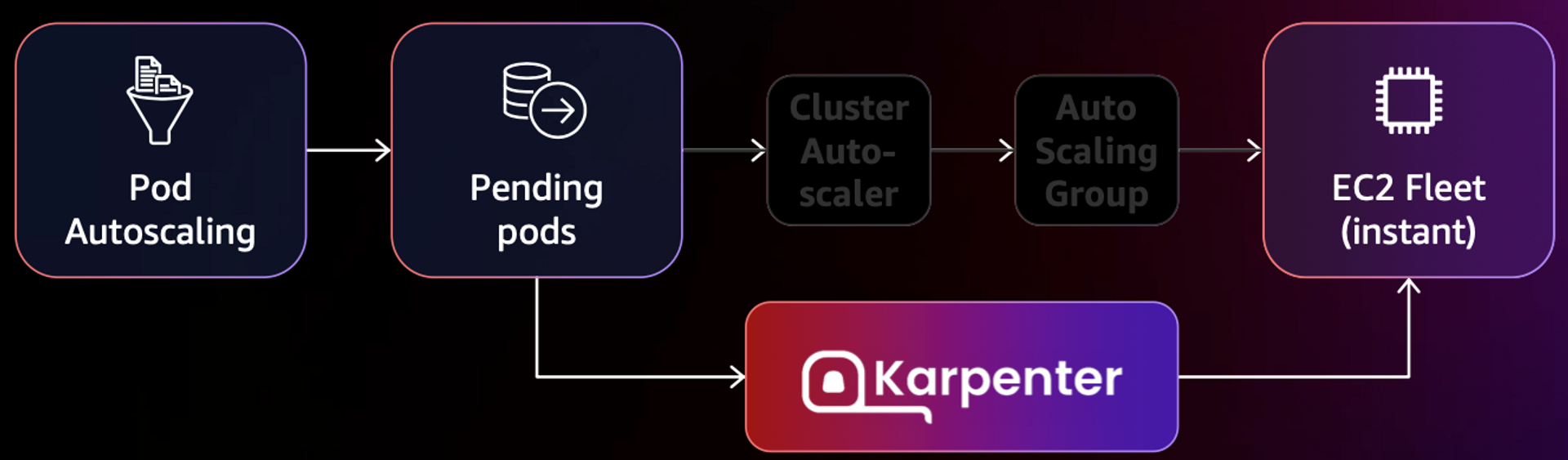
6. Karpenter : K8S Native AutoScaler & Fargate

- 쿠버네테스 스케줄러가 실행할 수 없는(unschedulable)로 표시한 파드를 감시한다.
- 파드에 의해 요청된 스케줄링 제약 조건(리소스 요청, 노드 셀렉터, 애핀리티, 톨러레이션, 토폴로지 스프레드 제약 조건)을 평가한다.
- 파드의 요구 사항을 충족하는 노드를 프로비저닝한다.
- 파드를 새로운 노드에서 실행하도록 스케줄링한다.
- 노드가 더 이상 필요 없을 때 노드를 제거한다.
- Karpenter는 아키텍처, 리소스 제한 및 노드 조건에 따라 오토스케일링을 수행하여 가장 효율적인 노드를 프로비저닝한다.
- 클은 관리형 컴퓨팅 서비스를 사용하여 클러스터에 추가적인 연산 리소스를 제공하고 리소스 사용량을 최적화한다.
'AWES[1기](Amzaon EKS Study)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [AWES] 6주차 - EKS Security (0) | 2023.06.01 |
|---|---|
| [AWES] 4주차 - EKS Observability (0) | 2023.05.18 |
| [AWES] 3주차 - EKS Storage & Node 관리 (0) | 2023.05.10 |
| [AWES] 2주차 - EKS Networking (0) | 2023.05.03 |
| [AWES] 1주차 - Amzaon EKS 설치 및 기본 사용 (4) | 2023.04.27 |